In-Vitro Meat
Health Benefits:
-
regulate cholesterol
-
promote healthy learning and behavior in children
-
promote healthy cognition later in life
-
prevent depression
-
promote heart health
The average current ratio of omega-3s to omega-6s (the not-so-good fatty acids) is between 20:1 and 50:1. Fill your culture medium with omega-3s to fix that ratio and offset all kinds of health risks caused by this imbalance! (Mercola)

What do you want to add to your culture
medium?
Which Additives
do you want to put in your steak?
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Adipocytes & Collagen
don't forget!
Everything you add to your meat is good, in moderation. sometimes too much of a vitamin can cause serious health issues!

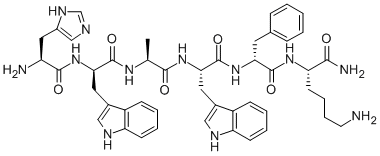

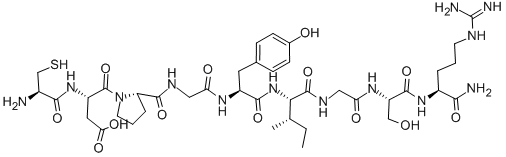
Omega-3
Fatty Acids
Adipocytes and Collagen
Farmers often give hormones to their animals to make them grow big and strong. This process is accelerated using biological molecules that are surprisingly similar to our own hormones. In small quantities, it's not much of a problem for our health (a lot of them end up being excreted anyways), but in large quantities, it is possible that overexposure to these hormones might have some dangerous biological effects for us humans! (Galbraith, 309-310)
Some of the most essential vitamins and minerals for our diets come from meat. Iron, Zinc, Vitamin B12, and Folate are among the most important. However, the reason why animal cells contain them is that they eat plants! These vitamins come from the animals' own diets, so adding algae or blue-green algae to your medium should allow the muscle cells to be full of the nutrients you need (Young et al, 908).
Did you know that the juicy, delicious texture and aroma which many know and love actually comes from the lipid profile of a piece of meat? Co-culture your sample with adipocytes (fat cells) and collagen (connective tissue) to recreate the experience of natural meat. Without this, your meat will taste quite bland and gritty. We are making food here, after all! (Young et al, 908)

